Introduction to Thick Sheet Vacuum Thermoforming Machine:
A thick sheet thermoforming machine (vacuum forming machine) is an advanced plastics processing equipment specifically designed for softening thick thermoplastic sheets (typically 0.8mm to 10mm thick) by heating them, then applying pressure to form them onto a mold surface, producing a product with a specific shape upon cooling.
This machine primarily consists of a loading mechanism, a heating system, a forming station, a cooling system, a control system, and a reclaimer. The process involves feeding cut plastic sheets (such as ABS, HIPS, PC, PMMA, PETG, etc.) into a heating furnace, where they are evenly heated until softened. They are then quickly transferred to the forming station, where vacuum suction, air pressure, or compression molding are used to securely fit the mold cavity and precisely form the sheet. After rapid cooling and finalization, a robotic arm removes the finished product for trimming and subsequent processing.
The core advantage of thick sheet thermoforming machines lies in their efficient and precise processing capabilities, enabling them to quickly produce large products with complex structures, stable dimensions, and a high surface gloss. It is widely used in automobiles (such as bumpers, floor mats), home appliances (refrigerator liner, air conditioner shell), transportation, medical equipment (equipment shell), advertising light boxes, and aerospace.
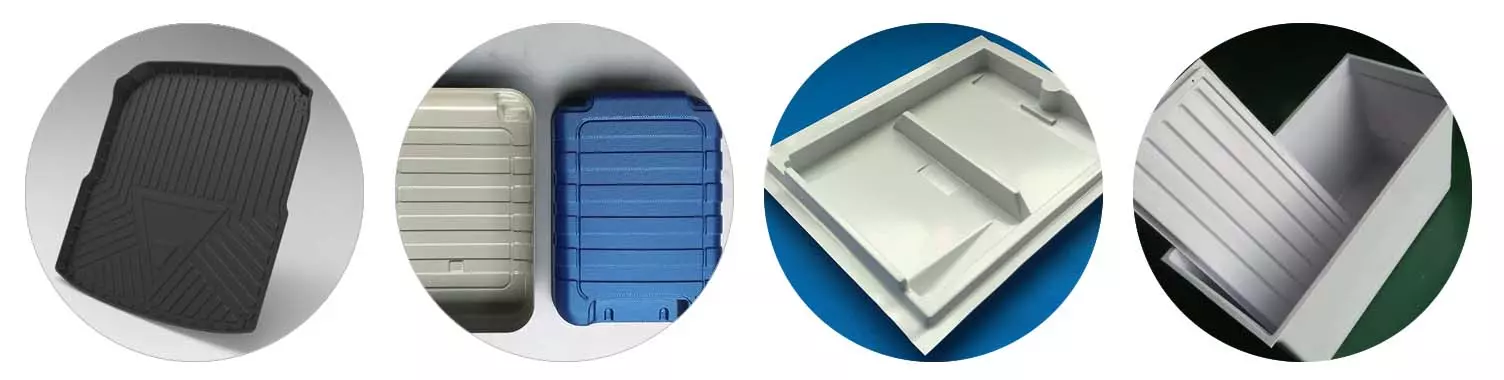
>> This machine is suitable for sheet materials such as ABS, PS, PVC, PE, PP, PC, and acrylic, and can be used to produce automotive floor mat interiors, medical device housings, refrigerator liners, bathtubs, and luggage.
>> Utilizing a PLC control system, all process parameters, operations, and settings are displayed on the touch screen. Automatic and manual modes can be switched independently, and a safety interlock function prevents damage from operator errors.
>> Utilizing a temperature control system with both digital and analog adjustments, parameters can be adjusted directly on the touch screen, and multiple data sets can be stored. The temperature of each heating unit in the heating zone is independently adjustable (one control, one precise control, more energy-efficient).
>> Utilizing fast medium-wave infrared heating elements, the unit can be turned on and off instantly, eliminating the need for preheating and achieving rapid temperature increases. The furnace only turns on when the heating station is reached. Dual electric heating furnaces, combined with a temperature controller and voltage regulator, ensure a constant heating temperature regardless of voltage fluctuations.
>> An anti-droop feature uses infrared light to monitor the heating status of the plastic sheet, preventing sagging during heating and uneven thickness of the finished product. The mold platform can be adjusted to any height, shortening mold change time and saving labor costs.
>> Pre-blowing and core pulling functions ensure more uniform thickness and higher quality for difficult-to-form products. A reverse blow demolding device allows for easy demolding of difficult-to-release molds, minimizing damage caused by mold release.
>> Dual cooling with a powerful fan and spray spray ensures faster and better product finalization, minimizing inferior product quality, accelerating cooling, and improving production efficiency.
| model |
SWT-1000d |
SWT-760s |
| Mold size(max.) |
1500~2500(mm)_Customizable |
1500*700(mm)_Customizable |
| Sheet specifications |
0.8~10mm |
0.8~5mm |
| Cooling method |
Air cooling + spray |
Air cooling + spray |
| Production efficiency |
1~4次/min(Depends on the product) |
1~8次/min(Depends on the product) |
| Control method |
PLC control |
PLC control |
| Applicable materials |
ABS,PET,PP,HIPS,PVC,PMMA.... |
ABS,PET,PP,HIPS,PVC,PMMA.... |
| Mold forming method |
Concave and convex mold heating molding |
Concave and convex mold heating molding |
| Maximum power |
95kw |
56kw |
| Power supply voltage |
380V50Hz(Three-phase four-wire) |
380V50Hz(Three-phase four-wire) |
| Equipment size |
4100*2500*3000(mm) |
4000*1400*3100(mm) |
01.
PLC intelligent control
Adopting PLC control system, all process parameters, operations and settings are displayed on the touch screen, which can be switched between automatic and manual states freely. Adopting temperature control system, digital analog adjustment, parameters can be adjusted directly on the touch screen, and multiple sets of data can be stored. The temperature of each heating unit in the heating zone is independently adjustable (the heating elements outside the mold can be turned off to save energy)
02.
Infrared heating, precise temperature control
The latest carbon fiber infrared heating tubes are used, which can be turned on and off at any time, without preheating, and heat up quickly. The electric furnace is turned on only when entering the heating station, and the power is turned off when the furnace is exited to achieve energy saving. The upper and lower double electric furnaces are used for heating, combined with a temperature control voltage regulator, the heating temperature is stable and will not change due to voltage fluctuations. The anti-droop function is used, and infrared monitoring of the heating status of the plastic sheet prevents the sheet from sagging due to heat during the heating process, resulting in uneven thickness of the formed product.
03.
Not Just Traditional Cyber & Immigration Firm
The pre-bubble and core-pulling functions ensure even thickness and improved quality for difficult-to-form products. A reverse-blowing air demolding device and multi-speed pulses facilitate demolding, minimizing mold damage and improving product yield. Secondary adjustable vacuum flow and vacuum delay allow for flexible control of different materials during vacuum forming. The mold platform can be adjusted in height to shorten mold changeover time and save labor costs.
The basic operating principle of a thick sheet thermoforming machine is similar to that of a conventional thin sheet thermoforming machine, forming the plastic sheet through three stages: heating, stretching, and cooling. First, the plastic sheet is heated to a softened state and evenly laid out on the forming area. Subsequently, airflow, either through negative pressure or positive and negative pressure, stretches the plastic sheet onto the mold surface. Finally, cooling and demolding complete the forming process.
Since the plastic sheets processed by the thick sheet thermoforming machine are relatively thick, the required heating and forming time is relatively long. Therefore, the heating system, control system and forming mold design of the equipment need to have higher precision and stability.

I. Key Technical Advantages
The widespread use of thick sheet thermoforming machines stems from a series of significant technical advantages:
Powerful 3D forming capabilities: They can produce large products with complex surfaces and deep cavities, which are difficult or extremely costly to achieve with other plastic processing methods (such as injection molding).
Relatively low mold costs: Compared to injection molding, which requires steel molds that withstand high pressure, thick sheet thermoforming typically uses molds made of gypsum, resin, aluminum alloy, and other materials. This results in a short manufacturing cycle and low cost, making it particularly suitable for small-batch, high-variety production.
Flexible product wall thickness control: By adjusting the initial sheet thickness, products with varying wall thicknesses can be easily produced. Furthermore, during the molding process, precise temperature control of the heating zone allows for fine-tuning of wall thickness in different areas of the product.
High material utilization and production efficiency: Using sheets with optimized cutting areas reduces scrap. The short molding cycle, ranging from tens of seconds to minutes, enables efficient, continuous production.
The products have high strength and beautiful appearance: the formed products maintain the toughness of the original board and have a smooth surface. They can be directly processed by spraying, laminating and other secondary processes to obtain excellent appearance effects.
II. Key Components Analysis
A modern thick sheet thermoforming machine is a sophisticated system integrating mechanical, electrical, vacuum, and temperature control technologies. Its main components include:
Frame and Clamping System: A sturdy frame is the foundation for stable operation. A robust clamping frame securely holds the sheet material in place, preventing it from shifting or deforming during the heating and forming process.
Heating System: This is the "energy heart" of the machine. It typically utilizes multi-zone ceramic far-infrared heaters, each with independent temperature and power adjustment for the most precise and uniform heating of the sheet material.
Forming System: This includes the upper and lower clamping mechanisms, the mold mounting platform, and the vacuum/compressed air system. The clamping mechanism requires smooth operation and precise positioning. The vacuum system must provide sufficient flow and vacuum to ensure fast and powerful suction forming.
Electrical Control System: Modern thick sheet thermoforming machines commonly utilize PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and touchscreen human-machine interfaces. Operators can easily set and store process parameters (such as heating time, temperature, and molding speed) for various products, enabling fully or semi-automatic production and ensuring product consistency and stability.
Cooling System: An efficient cooling system can significantly shorten production cycle times and is typically comprised of a high-power fan or water-cooled circulation system.
As an efficient, economical, and flexible plastics processing machine, thick sheet thermoforming machines have become an indispensable key piece of equipment in modern manufacturing. With their powerful shaping capabilities, they continue to transform flat sheets of plastic into practical and beautiful three-dimensional products, driving innovation and development in industrial design and manufacturing technologies.





